How Smart Cities & IoT Will Change Our Communities
3 min read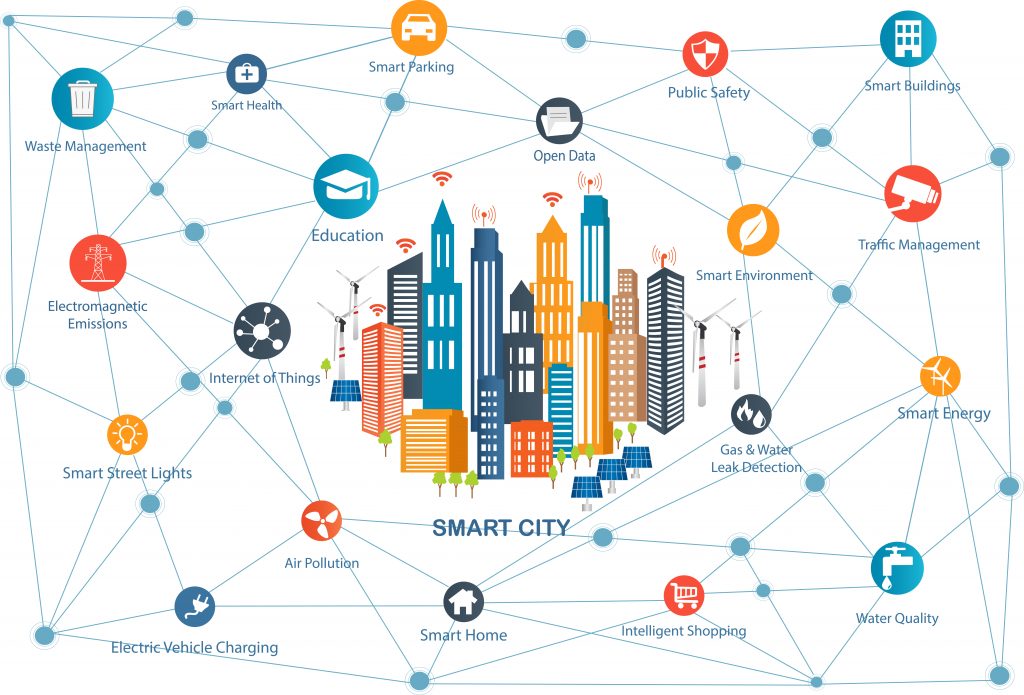
You’ve probably heard of IoT and how it’s linking people in innovative ways.
The advent of home automation is one example of how the Internet of Things is transforming people’s lives – houses packed with technology that can interact with one another and with the residents who stay there.
IoT has changed the lives of many people and change be used in medical care. With the help of IoT, we have achieved a lot.
How Smart Cities & IoT Will Change Our Communities
Smart City, also known as SCCs are being made possible by the IoT. In your personal and professional life, the number of data-sharing gadgets is rapidly increasing.
Environment at Home
Residents of Smart Buildings will have access to up-to-date power data, like present energy costs, supply, weather reports, and so on.
To better control, energy use across the local, city services will connect to equipment in the home, like solar cells, smart energy meters, car charging points, traffic cone, and home devices.
The introduction of health monitoring gadgets that can immediately inform relatives and city authorities of health crises will make caring for older family members easier.
City Environment
A Smart Town will assist its residents in making decisions ranging from where to spend their income to where to have dinner.
Businesses will be able to determine where to open up new eateries, department shops, dry cleaners, and other enterprises by measuring foot traffic throughout the city.
Visualizations showing dilapidated structures and regions that have to be restored will be created using GPS-tagged pictures supplied by city personnel and residents.
Allergy and asthma sufferers can plan routes around the town that do not aggravate their problems.
People in many nations are currently participating in a trial initiative in which they install monitors in their houses and workplaces and information gathered from Geolocation inhalers worn by a group of people is being used to link pollution levels and allergens around the city.
Infrastructure Care and Monitoring
Architecture in many cities throughout the world is deteriorating. The state of the roads is deteriorating. Train tracks are deteriorating. Major roads and bridges are deteriorating and becoming dangerous.
IoT software can be used to implant monitors in such locations to identify a variety of things, like the level of damage, weekly traffic flow changes, temperature anomalies that may accelerate deterioration, safety concerns that can result in mass accidents, and more.
Simply said, towns and localities may use IoT technologies to monitor the status of the facilities and administer those assets, resulting in advances in safety, cost of repairs, regularity, and more.
Energy Conservation
Your towns are consuming more power than ever before. The majority of this power comes from non-renewable fuels like coal.
Although cities with fairly renewable energy sources, like hydroelectric or nuclear electricity, might gain from lower raw consumption.
IoT technology has enormous potential for reducing energy use, particularly in areas like wasted electricity lights and unoccupied heating/cooling spaces. Cities may drastically reduce their demands on the energy system by concentrating on zoned light, warming, and cooling.
Better Communication Skills
The invention and deployment of smart networking provide for better communication skills from nearly any location within a metropolis. Traffic signals, for example, can connect with the town council or other responsible bodies, and public park grids can interact with the park service.
Parking
Smart parking systems assess whether parking places are filled or vacant using Gps locations from drivers’ phones (or road devices placed on the surface of parking places) and build a real-time car park chart.
Users receive a message when the nearest parking place becomes available, and rather than wandering around aimlessly, they utilize the GPS on the smartphone to locate a parking space easily.
Information from IoT devices can be used to uncover patterns in how citizens use public transportation.
This information can be used by public transit providers to improve the traveling experience, and also improve safety and timeliness. Smart public transportation systems can combine different sources, like ticket revenue and traffic data, to perform more complex analyses.
Conclusion
IoT’s potential is limitless. It offers services in different industries, including industry, fashion, restaurants, healthcare, and education.
Smart towns can use a single platform, which sounds plausible for smaller towns in particular. By providing a platform focused on public data, the cloud-based aspect of IoT technology for Smart Cities is suitable.